ShellCheck¶
This guide explains how to run ShellCheck with CloudAEye.
Overview¶
ShellCheck is a widely used static analysis tool for shell scripts (Bash, sh, and similar shells). It helps developers detect syntax errors, semantic issues, and common pitfalls in shell scripts, improving script reliability, portability, and readability.
Why Use ShellCheck?¶
- Catch errors early: Detect common scripting mistakes such as unquoted variables, typos, or improper use of commands.
- Improve portability: Identify code that may not work across different shell environments.
- Best-practice enforcement: Suggest improvements for more readable, maintainable, and safe shell scripts.
- Clear explanations: Provides actionable warnings and hints, including links to detailed documentation for each issue.
- Integration-friendly: ShellCheck can be used from the command line, in CI/CD pipelines, or integrated into editors for real-time feedback.
- Lightweight and fast: Runs quickly, making it suitable for both small scripts and large shell-based projects.
ShellCheck is ideal for developers and DevOps engineers who want to write reliable, maintainable shell scripts while avoiding subtle bugs and security issues.
Prerequisites¶
Step 1: Register¶
Sign up with CloudAEye SaaS.
Step 2: Install GitHub App¶
Integrate with GitHub by installing the GitHub app.
Step 3: Connect Github Repositorie¶
Connect the repositories where you would like to use CloudAEye Code Review features.
Step 4: Configure the Linter¶
Configure the desired linter.
Configuration¶
CloudAEye supports a recommended configuration for ShellCheck.
If your repository already has ShellCheck configured, CloudAEye will automatically use that setup. You may also enter your desired configuration.
Use repo config¶
CloudAEye automatically reads your repository’s existing ShellCheck configuration and uses it as is. No additional setup is needed.
Common ShellCheck Configuration File Locations & Formats¶
1. Configuration file (.shellcheckrc)
ShellCheck can read a .shellcheckrc file from your project root or home directory. In this file, you can define:
- Rules to enable or disable
- Warning severity
- Include or exclude patterns
2. Inline directives in the script
You can configure ShellCheck directly in your shell script using comments:
# shellcheck disable=SC2086
some_command $UNQUOTED_VAR
Manual¶
You may enter the ShellCheck configuration you would like to use.
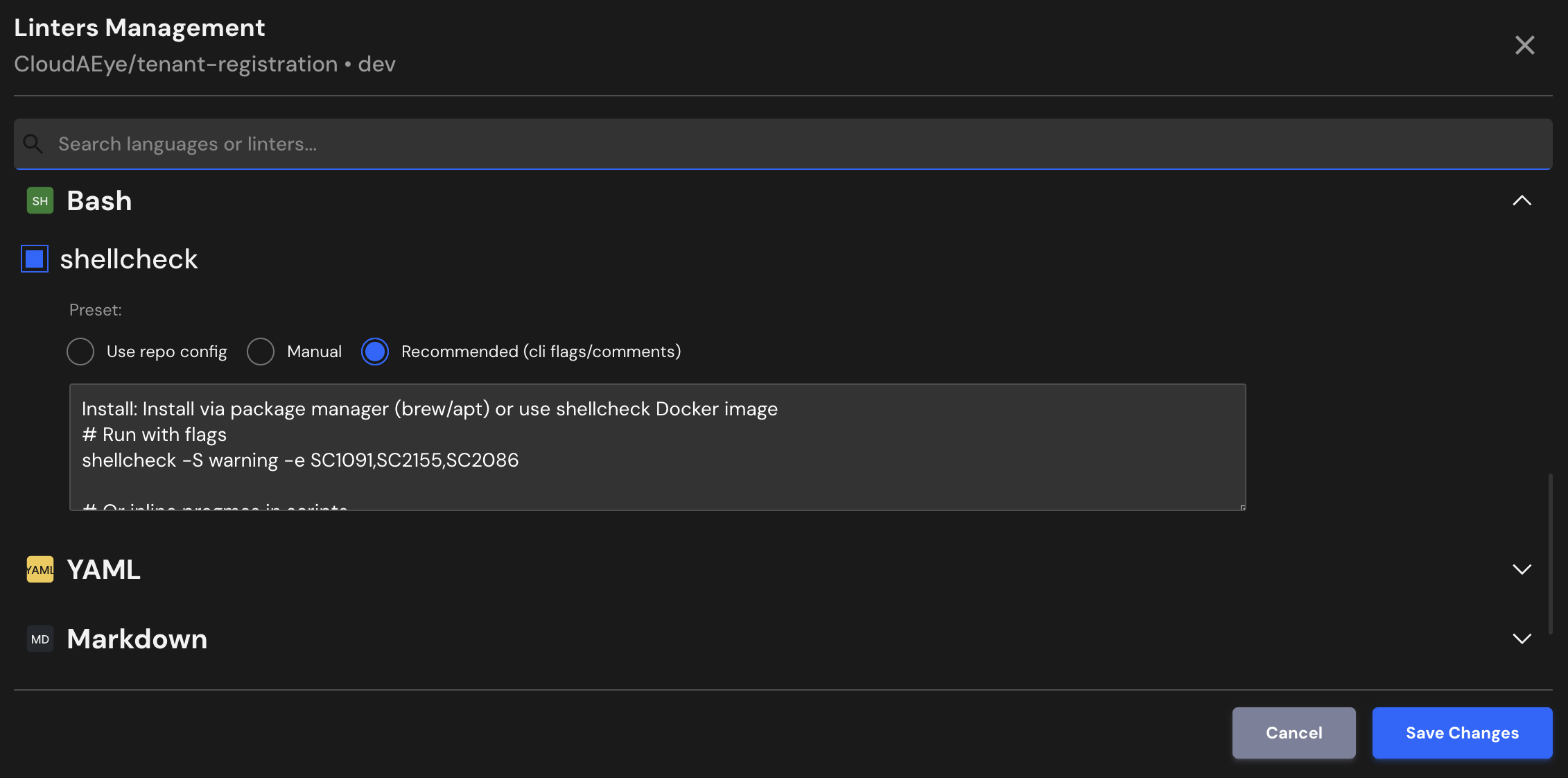
Recommended (cli flags/comments)¶
Install: Install via package manager (brew/apt) or use shellcheck Docker image
# Run with flags
shellcheck -S warning -e SC1091,SC2155,SC2086
# Or inline pragmas in scripts
# shellcheck disable=SC1091 # non-standard include
# shellcheck disable=SC2155 # variable declared in subshell
File Extensions¶
ShellCheck will run on files that use any of the following extensions:
.sh, .bash, .ksh, .dash