Ruff¶
This guide explains how to run Ruff with CloudAEye.
Overview¶
Ruff is an ultra-fast Python linter and code formatter, written in Rust, designed to provide both speed and power.
Highlights¶
- Lightning-fast performance: Ruff runs 10×–100× faster than many traditional Python linters and formatters like Flake8 or Black.
- All-in-one tool: It merges functionality from multiple tools—such as Flake8 (and many of its plugins), isort, pyupgrade, autoflake, and more—into a single, unified interface.
- Smart configuration: You can configure Ruff through pyproject.toml, ruff.toml, or .ruff.toml.
- Extensive rule set: It includes 800+ built-in linting rules, with native re-implementations of rules from popular linters and plugins (e.g., flake8-bugbear).
Prerequisites¶
Step 1: Register¶
Sign up with CloudAEye SaaS.
Step 2: Install GitHub App¶
Integrate with GitHub by installing the GitHub app.
Step 3: Connect Github Repositorie¶
Connect the repositories where you would like to use CloudAEye Code Review features.
Step 4: Configure the Linter¶
Configure the desired linter.
Configuration¶
CloudAEye supports Ruff’s recommended best-practice configuration. If your repository already has Ruff configured, CloudAEye will automatically use that setup.
Use repo config¶
CloudAEye automatically reads your repository’s existing Ruff configuration and uses it as is. No additional setup is needed.
Common Ruff Configuration File Locations & Formats¶
Ruff looks for configuration in this order:
1. pyproject.toml (recommended)
This is the most common and preferred location. Example section:
[tool.ruff]
line-length = 88
select = ["E", "F"]
2. ruff.toml
A standalone configuration file dedicated solely to Ruff.
3. ruff.ini or ruff.cfg
INI-style configuration files supported for flexibility.
4. setup.cfg
If your Python project already uses setup.cfg, Ruff can read configuration from a [tool.ruff] section there.
Manual¶
You may enter the Ruff configuration you would like to use.
Best Practice (pyproject.toml)¶
Places configuration in pyproject.toml at the project root.
Install: pip install ruff
[tool.ruff]
# Match your project's runtime version
target-version = "py311"
line-length = 100
extend-exclude = [
"migrations",
"tests/fixtures",
"build",
"dist",
]
# Enable rule sets
select = [
"E", # pycodestyle errors
"F", # pyflakes
"I", # isort import order
"B", # bugbear
"UP", # pyupgrade
"N", # pep8-naming
"SIM", # simplify
"RUF", # Ruff-specific rules
]
# Disable rules that are often too strict or stylistic
ignore = [
"E501", # line length (handled by formatter)
"B008", # function call as default arg
]
# Automatically fix what can be safely fixed
fix = true
unsafe-fixes = false
[tool.ruff.lint]
unfixable = ["F401"] # unused imports
[tool.ruff.format]
quote-style = "double"
indent-style = "space"
line-ending = "auto"
skip-magic-trailing-comma = false
docstring-code-format = true
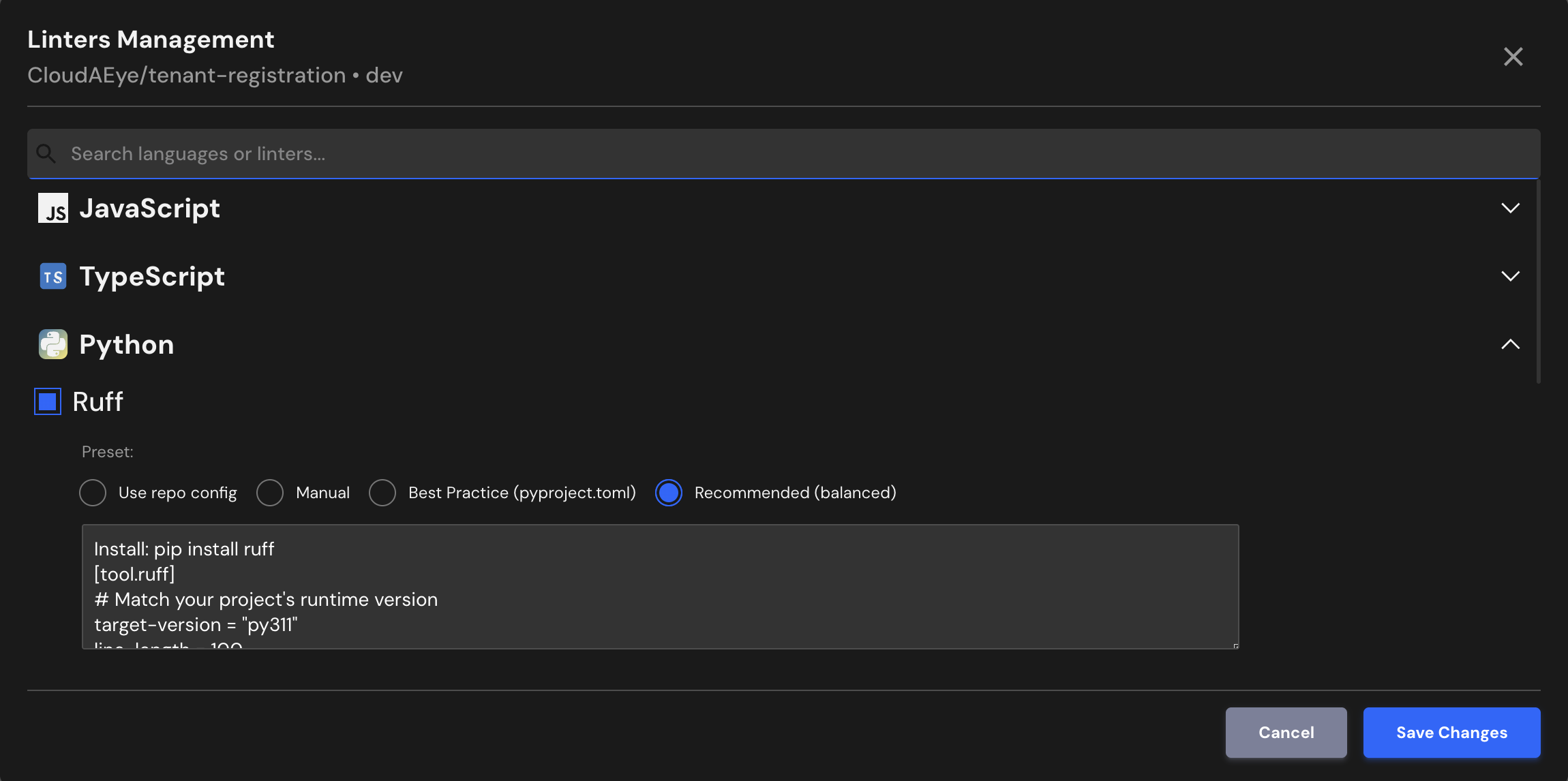
Recommended (balanced)¶
Install: pip install ruff
[tool.ruff]
# Match your project's runtime version
target-version = "py311"
line-length = 100
extend-exclude = [
"migrations",
"tests/fixtures",
"build",
"dist",
]
# Enable rule sets
select = [
"E", # pycodestyle errors
"F", # pyflakes
"I", # isort import order
"B", # bugbear
"UP", # pyupgrade
"N", # pep8-naming
"SIM", # simplify
"RUF", # Ruff-specific rules
]
# Disable rules that are often too strict or stylistic
ignore = [
"E501", # line length (handled by formatter)
"B008", # function call as default arg
]
# Automatically fix what can be safely fixed
fix = true
unsafe-fixes = false
[tool.ruff.lint]
unfixable = ["F401"] # unused imports
[tool.ruff.format]
quote-style = "double"
indent-style = "space"
line-ending = "auto"
skip-magic-trailing-comma = false
docstring-code-format = true
File Extensions¶
Ruff will run on files that use any of the following extensions:
.py
References¶
- Ruff tutorial
- Ruff configuration
- Ruff project