ESLint¶
This guide explains how to run ESLint with CloudAEye.
Overview¶
ESLint is a linting tool used to analyze and improve JavaScript, TypeScript, JSX, TSX, CSS, and similar code.
ESLint is a powerful and widely used linting tool for JavaScript and TypeScript. It helps developers identify and fix problems in their code by enforcing consistent style, catching common errors, and promoting best practices. ESLint is fully configurable, allowing teams to define their own coding standards or adopt well-known community style guides.
ESLint works by analyzing your code’s abstract syntax tree (AST) and applying a set of rules to detect issues such as unsafe patterns, unused variables, incorrect syntax, or deviations from your chosen style conventions. It integrates seamlessly with modern development workflows, including popular editors, build systems, and CI pipelines.
Because ESLint is highly extensible, you can enhance it with plugins, custom rules, shareable configs, and framework-specific presets.
Prerequisites¶
Step 1: Register¶
Sign up with CloudAEye SaaS.
Step 2: Install GitHub App¶
Integrate with GitHub by installing the GitHub app.
Step 3: Connect Github Repositories¶
Connect the repositories where you would like to use CloudAEye Code Review features.
Step 4: Configure the Linter¶
Configure the desired linter.
Configuration¶
Several widely adopted ESLint configurations are recognized as best-practice baselines, and CloudAEye supports all of them. If your repository already includes its own ESLint setup, CloudAEye will automatically use that configuration as well.
Use repo config¶
CloudAEye automatically reads your repository’s existing ESLint configuration and uses it as is. No additional setup is needed.
Common ESLint Configuration File Locations & Formats¶
ESLint looks for configuration in the following files (in order of preference):
eslint.config.js(the new Flat Config format)eslint.config.mjs/eslint.config.cjs- Legacy config formats (still widely used):
.eslintrc.js.eslintrc.cjs.eslintrc.json.eslintrc.ymlor.eslintrc.yaml
Typical Location: Place the ESLint configuration file at the root of your project repository, alongside files like package.json.
Manual¶
You may enter the ESLint configuration you would like to use.
eslint:recommended¶
Enables a set of core rules that catch common problems (like no-unused-vars, no-undef).
Good baseline, but minimal.
{
"extends": "eslint:recommended"
}
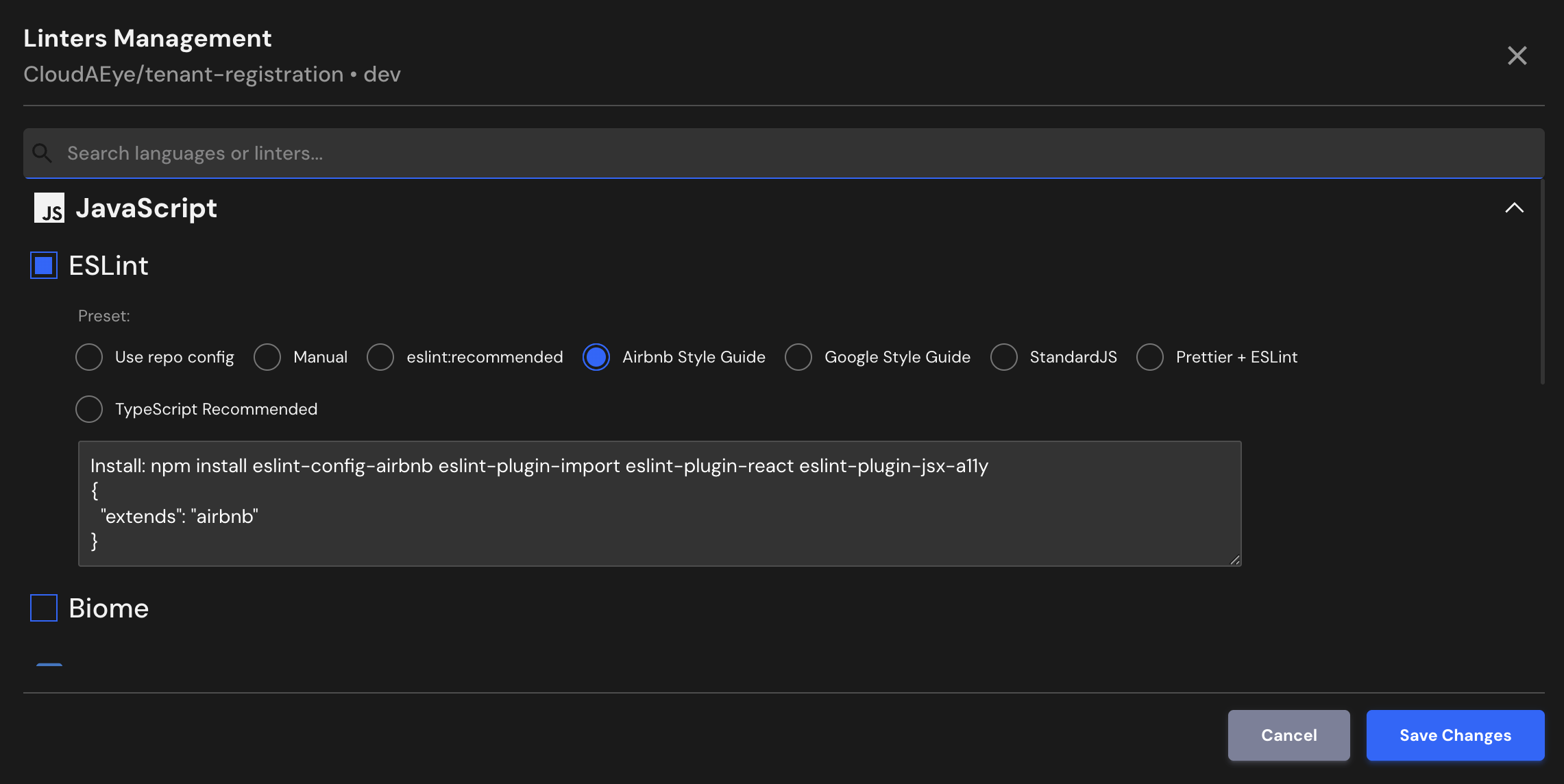
Airbnb Style Guide¶
One of the most popular style guides. Strong opinions on formatting, React, and imports. Great for consistency across teams.
Install: npm install eslint-config-airbnb eslint-plugin-import eslint-plugin-react eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y
{
"extends": "airbnb"
}
Google Style Guide¶
Based on Google’s JavaScript style guide. Less strict than Airbnb, but still opinionated.
Install: npm install eslint-config-google
{
"extends": "google"
}
StandardJS¶
No semicolons, minimalist rules. Good for smaller projects or teams that want simplicity.
Install: npm install eslint-config-standard eslint-plugin-import eslint-plugin-n
{
"extends": "standard"
}
Prettier + ESLint¶
If you use Prettier for formatting, you should disable conflicting ESLint rules.
Use eslint-config-prettier to ensure ESLint only handles logic, not formatting.
Install: npm install eslint-config-prettier
{
"extends": ["airbnb", "prettier"]
}
TypeScript Recommended¶
For TypeScript, you should extend ESLint with TypeScript rules.
Recommended config is:
Install: npm install --save-dev @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin
{
"parser": "@typescript-eslint/parser",
"extends": [
"eslint:recommended",
"plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended",
"prettier"
],
"plugins": ["@typescript-eslint"]
}
File Extensions¶
ESLint will run on files that use any of the following extensions:
.js, .ts, .cjs, .mjs, .d.cts, .d.mts, .jsx, .tsx, .css, .vue, .svelte, .astro
References¶
- ESLint Getting Started guide
- ESLinkt architecture