Manage Storage¶
Overview¶
CloudAEye offers three different storage tiers: hot, UltraWarm, and cold.
- If you’re looking for the fastest performance when indexing and searching data, hot storage is the best option. It provides low latency and fast access to your data.
- UltraWarm is a cost-effective option that provides read-only access to data you may query less frequently. It’s a great choice if you don’t need the same performance as hot storage.
- Cold storage is optimized for storing historical data. You can rehydrate these data indexes if you need to query them. You can store any amount of data in cold storage, and it’s the most cost-effective option.
You may define a policy to automatically move logs to cheaper storage as they age. This topic describes how to achieve that.
Prerequisites¶
While creatng the logs service, user must enable UltraWarm and Cold storage options. Manage Storage tab will appear in Service Details UI for a logs service if you enable the storage tiers.
Policy Based Aging¶
You may define a policy to automatically move data between storage tiers.
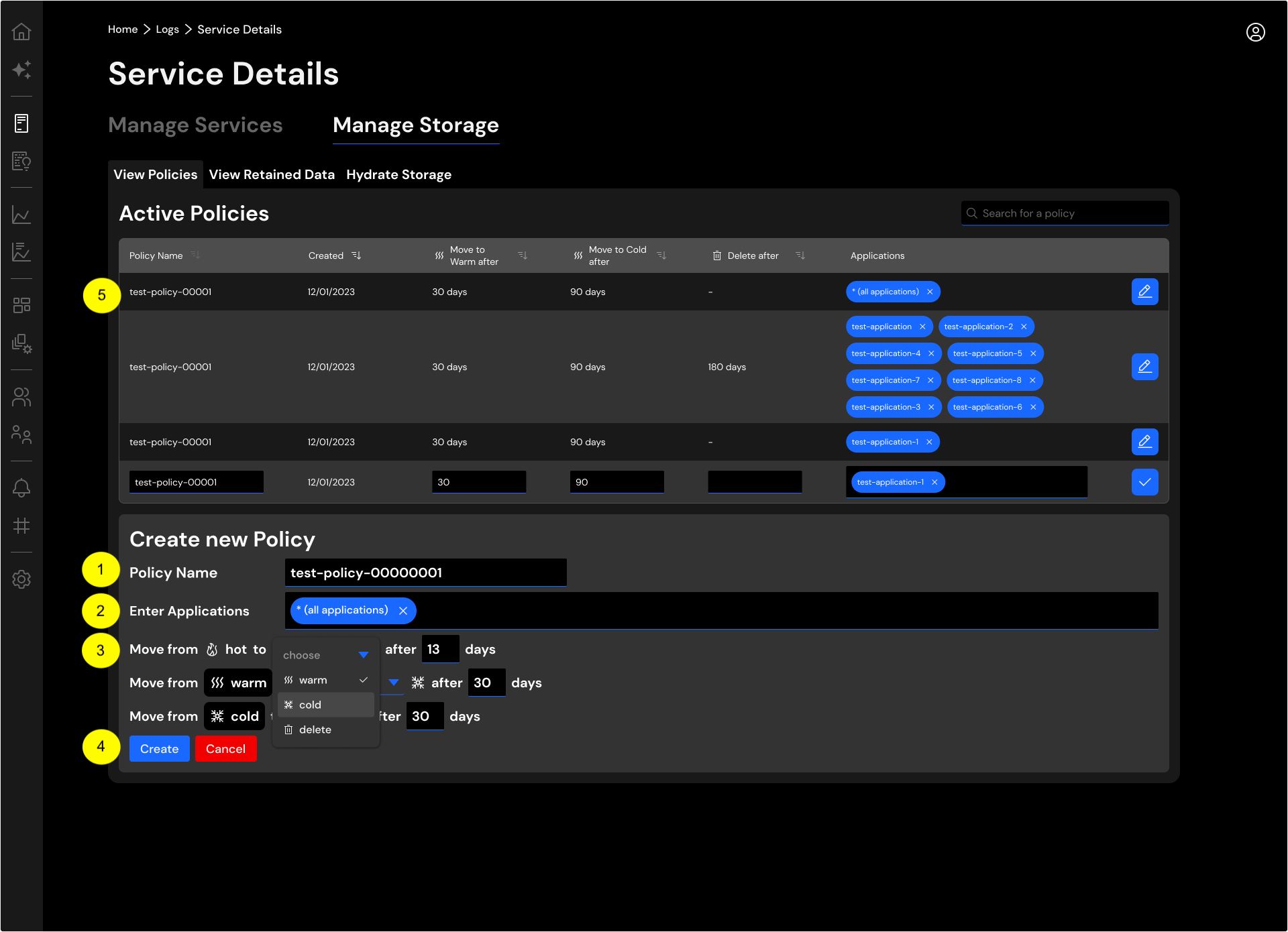
To create a policy, you may provide the following:
- Policy Name: Name of this storage policy.
- Enter Applications: This defines the scope of the policy. You may use
*for all applications. Otherwise, list the specific application(s). - Move from: You may use this section to define how data moves between hot, UltraWarm, cold storage and eventually deleted. You may choose the retention period.
- Create: Click the
Createbutton to create the policy. - You may see all active policies you have defined for the logs service. This shows when the policy was created, retention period for each storage tier and scope.
Impact on Billing¶
CloudAEye log ingestion per day offer rates based on 3, 7, 14, 30 and 45 day. Your billing will be based on the storage policy and pricing plan that covers the storage policy.
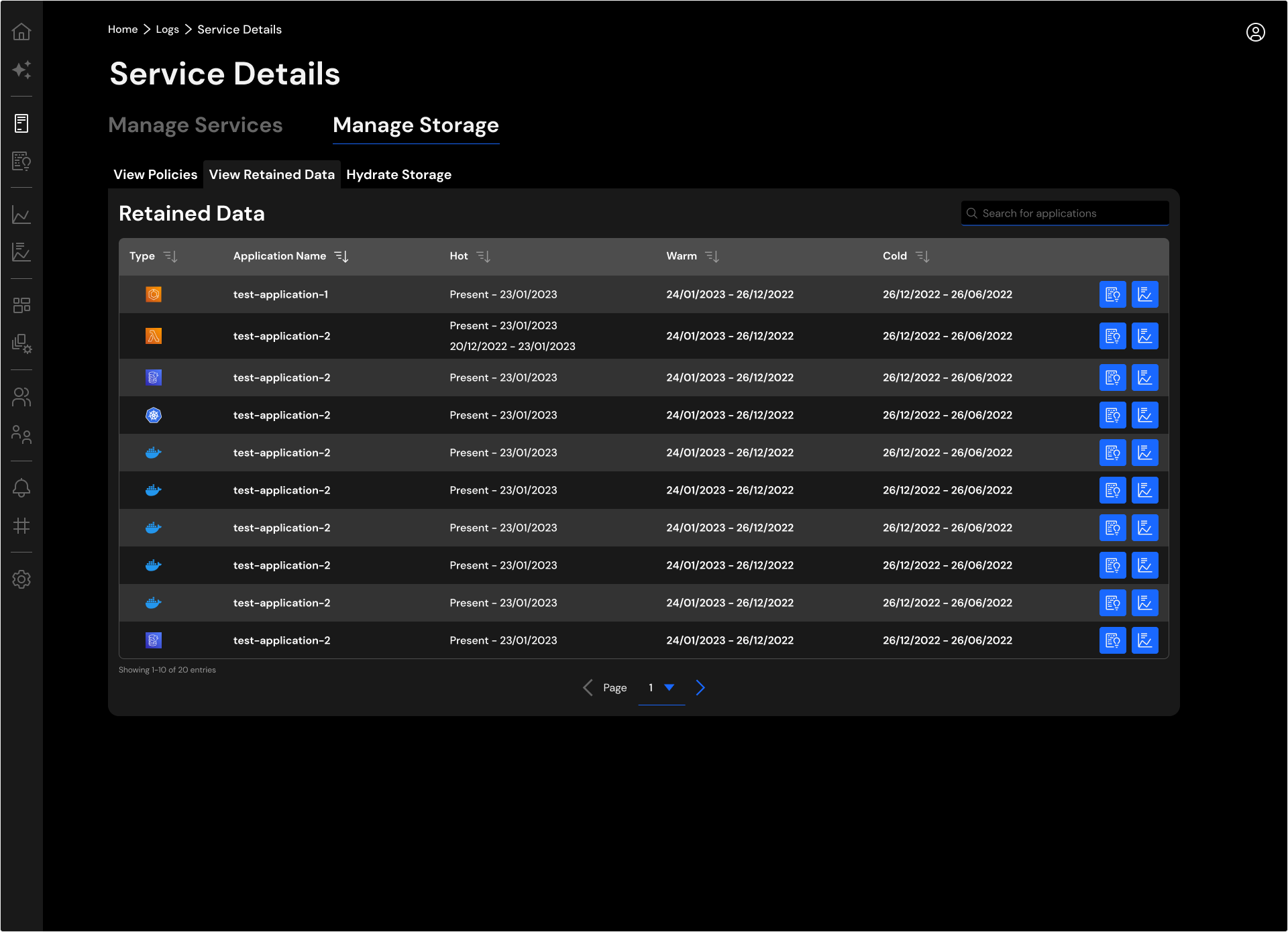
Retained Data¶
View Retained Data tab shows all the data per application in different storage tiers. You may query all data in hot and UltraWarm. For the data in cold storage, you may rehydrate specific indexes based on the date range.
Hydrate Storage¶
You may re-hydrate data from any storage tiers into hot or UltraWarm.
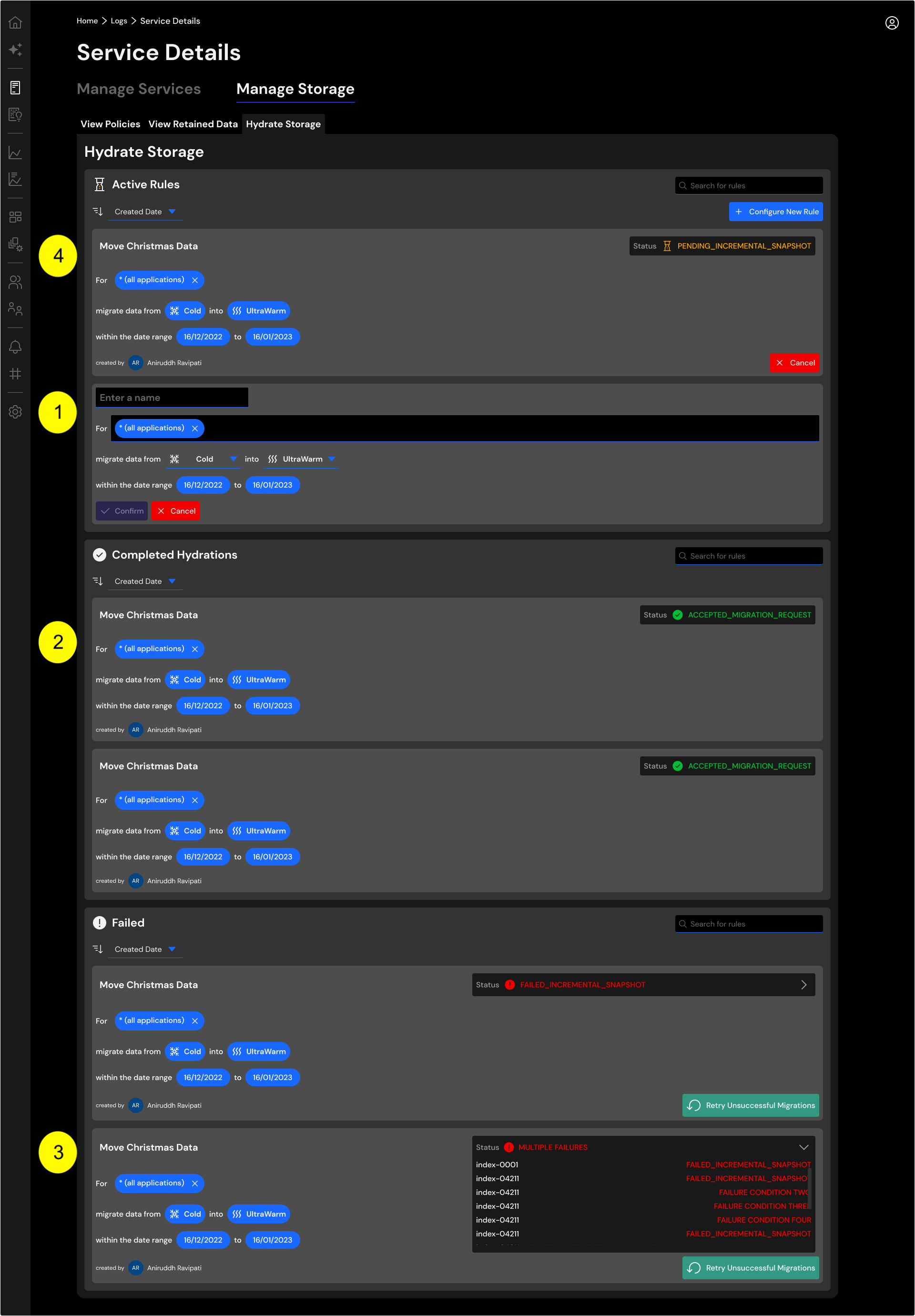
The Hydrate Storage tab shows the following:
- To initiate re-hydration, you may define the scope (application names),
fromandtoof the target migration and a date range for the data you want to move. - Shows successfully completed data hydration.
- Shows data hydration that ran into errors. You may re-try moving the data by clicking on the
Retry Unsuccessful Migrationbutton. - Shows ongoing data hydration activity.
Storage Estimation¶
CloudAEye uses the following equation to calculate hot storage size.
Hot Storage = (daily ingested data in bytes * 1.25) * (number of replicas + 1) * number of days retention
When you move data from cold to hot, please be mindful of how much data you are considering to move back in. You must not bring in more data than allocated storage.
Conclusion¶
CloudAEye provides three storage tiers: hot, UltraWarm, and cold. You can choose the best strategy to balance cost and performance based on your data retention, query latency, and budgeting requirements. You can also migrate data between different storage tiers.